Lung Cancer Symptoms
Common lung cancer symptoms include a cough, difficulty breathing, and loss of appetite. Some patients may have these symptoms early on, while others might not develop symptoms until the cancer has spread through their bodies. If you or a loved one has possible lung cancer symptoms, see a doctor immediately.
What Are the Signs and Symptoms of Lung Cancer?
As lung cancer spreads and overruns the body, people can experience a number of different symptoms.
- Coughing: People with lung cancer often have coughs that simply don’t go away. Coughing up blood or sputum (phlegm) is common.
- Difficulty breathing: People with lung cancer often find themselves out of breath after doing simple tasks, such as walking up the stairs.
- Finger clubbing: The tips of lung cancer patients’ fingers may become boxy or sqaureish in a process known as finger clubbing.
- Infections: People with lung cancer may develop infections such as pneumonia and bronchitis that won’t go away or keep on returning.
- Pain in the bones: Lung cancer patients may experience bone pain once the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
- Weight loss and loss of appetite: Lung cancer can change your appetite, causing you to feel less hungry and in turn lose weight.
If you or a loved one has any of the lung cancer symptoms listed above, make sure to get medical attention from a specialist. Health care providers can see if these symptoms are stemming from lung cancer or not and recommend treatments.
Get our Free Lung Cancer Guide now if your loved one has symptoms of this disease. You can learn how to manage symptoms and get the treatments needed to live longer.

- Understand risk factors
- Find top treatments
- Pursue compensation




What Causes Lung Cancer Symptoms?
The main reason people develop lung cancer symptoms is that the cancer has spread through their body, imparing its normal functions.
For example, the Mayo Clinic notes that patients can suffer from difficulty breathing if lung cancer tumors spread into the body’s main airways. Patients might also start to cough up blood as lung cancer tumors can cause internal bleeding.
When there’s severe metastasis (spread), lung cancer tumors can reach areas like the bones (causing pain) or brain (leading to headaches, nausea, and other symptoms).
Doctors can help explain how lung cancer is causing your symptoms and recommend a treatment plan after you’re formally diagnosed.
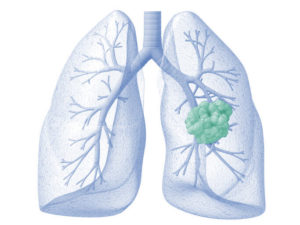
Symptoms by Lung Cancer Type
There are two main types of lung cancer: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and small cell lung cancer (SCLC). However, both of these types have similar symptoms, according to the Moffitt Cancer Center and Yale Medicine.
Common symptoms of both NSCLC and SCLC include:
- Blood in sputum
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Cough that won’t go away/gets worse over time
- Fatigue
- Hoarseness
- Loss of appetite
- Pain in bones, shoulder, other areas
- Shortness of breath
- Trouble swallowing
- Swelling in the face and neck veins
- Unexplained weight loss
Besides these two main lung cancer types, there are also a couple of rare subtypes of lung cancer that can cause more unique symptoms.

Lung carcinoid tumors are another rare type of lung cancer. They tend to grow slower than other types of lung cancer. Unique symptoms of lung carcinoid tumors include diarrhea, weight gain, and purple or pink marks on the skin that resemble stretch marks.
Learn about the symptoms of different types of lung cancer, and the treatments that can help you or a loved one, in our Free Lung Cancer Guide.




- Understand risk factors
- Find top treatments
- Pursue compensation




Lung Cancer Symptoms by Stage
Doctors classify cases of lung cancer into several stages depending on how far the tumors have spread. Most patients won’t have noticeable symptoms until they are in the advanced stages of lung cancer. However, some people experience symptoms in the early stages of lung cancer.
There are different stages depending on which type of lung cancer a patient has. Learn about the symptoms that can appear at each lung cancer stage below.
Small Cell Lung Cancer Symptoms and Stages
SCLC can be described in two stages: limited and extensive.
![Limited-stage SCLC]()
Limited-stage SCLC
Limited-stage SCLC only develops in one lung and does not spread to the mediastinum (area between the lungs) and the lymph nodes. Because of this, patients usually do not have lung cancer symptoms at this stage.
![Extensive-stage SCLC]()
Extensive-stage SCLC
Extensive-stage SCLC has spread to tissue outside of the lung that was originally affected, such as the opposite lung and other organs. In this stage, patients can exhibit symptoms like a cough, difficulty breathing, chest pain, and more.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Symptoms and Stages
Cases of NSCLC can be classified into one of five stages (stage 0 to stage 4). Typically, the symptoms are more severe in the later stages.

Stage 0 Lung Cancer Symptoms
At this stage, the cancer is only in the top lining of the bronchus or lung. It has not spread. Because of this, it’s likely that patients will have little to no lung cancer symptoms at this stage.

Stage 1 Lung Cancer Symptoms
In stage 1, the cancer has not yet spread to the lymph nodes and other organs. Like in stage 0, most patients in this stage won’t have symptoms of lung cancer.
When patients do have symptoms, they include a new and persistent cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, and lung infections, according to City of Hope.

Stage 2 Lung Cancer Symptoms
Stage 2 tumors may be slightly larger than those in stage 1 and have begun to spread to nearby lymph nodes. However, the cancer has not yet spread to other organs.
The lung cancer symptoms at this stage include many of those found in stage 1 (cough, pain in the chest, and difficulty breathing). Patients with this stage often don’t have symptoms, though.

Stage 3 Lung Cancer Symptoms
By this stage, the cancer has already spread to the lymph nodes of the mediastinum. It may also be found in other body parts beyond the lungs. For these reasons, it’s likely that patients will start having lung cancer symptoms in this stage if they haven’t already.
Stage 3 lung cancer symptoms can include weight loss, fatigue, dizziness and seizures, bone pain, and numbness in the arms or legs, in addition to the symptoms from the earlier stages. Which symptoms a patient will experience depends on where the cancer has spread to.

Stage 4 Lung Cancer Symptoms
This is the most advanced stage of NSCLC. By this point, the cancer has already metastasized (spread) to the lung lining and throughout the body.
Patients may suffer severe symptoms like limb numbness, headaches, jaundice, pain in the bones, swollen lymph nodes, severe chest pain, coughing, and difficulty breathing. As in stage 3, the cancer can spread to several different parts in the body, causing specific symptoms based on where it ends up.
How Are Lung Cancer Symptoms Diagnosed?
If you have possible lung cancer symptoms, see a doctor and report your concerns to get a diagnosis.
When you meet with your doctor, be sure to tell them:
- Which lung cancer symptoms you have
- When these symptoms developed
- If the symptoms have been getting worse
You can also tell your doctor if you were ever smoked or were exposed to asbestos, radon, secondhand smoke, or other toxins. Any and all of these can cause lung cancer. Doctors can use this information to rule out other possible causes of your symptoms.
“If you go to your doctor when you first notice symptoms, your cancer might be diagnosed at an earlier stage, when treatment is more likely to be effective.”
— American Cancer Society
Medical professionals typically use a low-dose computed tomography (CT) scan or a chest X-ray to conduct a lung cancer screening.
If doctors find tumors that could be causing your symptoms on these scans, they’ll then take a biopsy (sample) of them. A biopsy will allow the doctors to confirm your lung cancer diagnosis.
Treatment for Lung Cancer Symptoms
Doctors typically treat lung cancer and its associated symptoms in two main ways.
The first way is to use life-extending lung cancer treatments. The main goal here is to help the lung cancer patient live longer and with fewer symptoms.
Common life-extending treatments for lung cancer include chemotherapy, surgery, and radiation therapy, all of which can help shrink or remove cancer tumors. In doing so, the patient should see their lung cancer symptoms lessen or disappear. Major life-extending treatments are typically used for patients with early-stage lung cancer.

Common palliative treatment options for lung cancer symptoms include pain-relieving medications, supplemental oxygen and/or nutrition, and emotional counseling, according to the American Lung Association.
Get our Free Lung Cancer Guide now to find treatments that can ease symptoms and improve your survival time.




- Understand risk factors
- Find top treatments
- Pursue compensation




Get Help for Lung Cancer Symptoms
If you’re suffering from possible lung cancer symptoms, get professional cancer care as soon as possible. By connecting with top doctors, you can access treatments to ease symptoms of lung cancer and possibly become a survivor.
We at Lung Cancer Group may be able to help you access key resources, including financial aid, to support you on your cancer journey. Learn more by calling (877) 446-5767 or requesting our Free Lung Cancer Guide right now.
FAQs About Lung Cancer Symptoms
What are the first symptoms of lung cancer?
According to the Cleveland Clinic, the first symptoms of lung cancer are infections or a cough that keep happening despite treatment.
If you’re suffering from these symptoms and smoke, used to smoke, or were exposed to cancer-causing substances like asbestos, see a doctor.
What are some symptoms of asbestos-caused lung cancer?
The symptoms of lung cancer caused by asbestos are the same as any other type of lung cancer. Patients may suffer from a cough that doesn’t go away, shortness of breath, chest pain, and appetite loss.
However, those with asbestos lung cancer may qualify for additional financial aid that’s not available to other patients. Learn more by calling (877) 446-5767 now.
How does a doctor diagnose lung cancer symptoms?
Doctors will take note of any possible lung cancer symptoms that you have and then conduct a physical examination. If they still believe that a lung cancer tumor is to blame for your symptoms, they’ll likely use imaging scans to look inside your body.
Then, they’ll conduct a biopsy to extract a sample of possibly cancerous fluid or tissue. The biopsy will be sent to a lab, where pathologists will look at it under a microscope and see if lung cancer cells are present.
If so, doctors will confirm that your symptoms are indeed caused by lung cancer.
Are lung cancer symptoms the same as mesothelioma symptoms?
Lung cancer shares many symptoms with pleural mesothelioma, a cancer that affects the lung lining first before spreading into the lungs. Common symptoms shared by both illnesses include shortness of breath, a lingering cough, and weight loss.
However, mesothelioma can develop in other parts of the body, not just the lung lining. In these cases, patients may experience symptoms that aren’t similar to lung cancer symptoms, like abdominal swelling and constipation.
Doctors can confirm if your symptoms stem from lung cancer, mesothelioma, or another illness during the time of diagnosis.
Can pain in other parts of the body be related to lung cancer?
Possibly, yes. Advanced lung cancer that spreads may cause pain in other parts of your body. For example, pancoast lung cancer tumors can cause shoulder pain.
For best results, ask your doctor if any pain or other symptoms you’re experiencing could be related to lung cancer.